
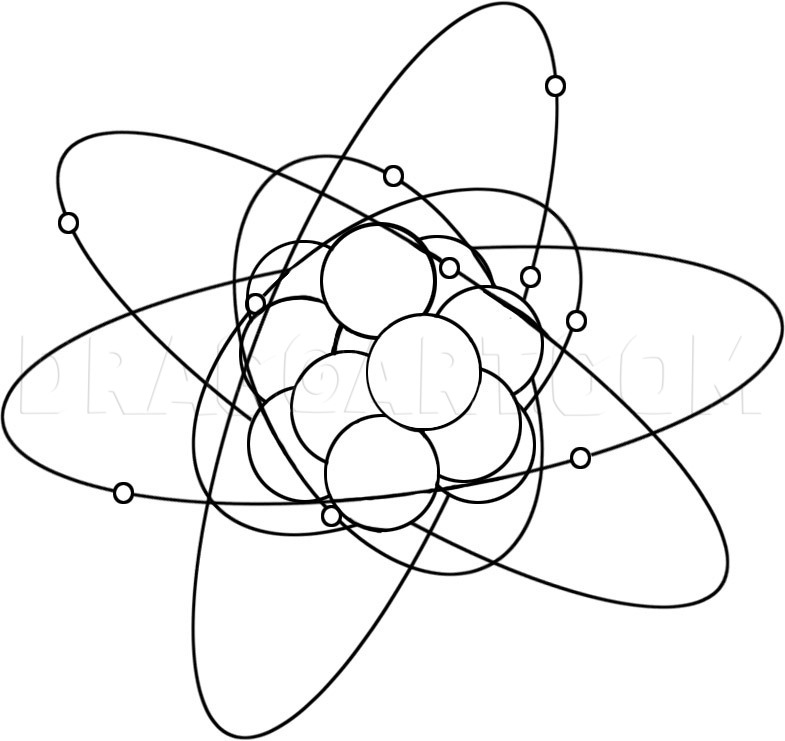
1.1.7 write and draw the electronic configuration (structure) of atoms and ions with atomic number 1–20.1.1.6 calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom or an ion and deduce the charge on an ion or determine the number of subatomic particles given the charge.Unit C1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis.1.1.8 write and draw the electronic configuration (structure) of atoms and ions with atomic number 1–20.1.1.7 calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom or an ion and deduce the charge on an ion or determine the number of subatomic particles given the charge.Unit 1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis.The mass number of an atom is equal to the number of protons added to the number of neutrons.In a neutral atom the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons.The number of protons in an atom is given by the atomic number.Protons and neutrons have an approximate mass of one atomic mass unit and electrons, in comparison, have virtually no mass. Protons have a charge of one-positive, neutrons are neutral and electrons have a charge of one-negative.An atom has a nucleus, containing protons and neutrons, and electrons that orbit the nucleus.The electron arrangement of the first 20 elements can be written.Atomic structure and bonding related to properties of materials.C1.2b describe the atom as a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons, with the nuclear radius much smaller than that of the atom and with most of the mass in the nucleus.C2.1.2 describe the atom as a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons, with the nuclear radius much smaller than that of the atom and with most of the mass in the nucleus.C2.1 How have our ideas about atoms developed over time?.1.2 Describe the structure of an atom as a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells.5.1.1.4 Relative electrical charges of subatomic particles.5.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes.5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table.Describe the atom as a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons, with the nuclear radius much smaller than that of the atom and with almost all of the mass in the nucleus.Recall that in each atom its electrons are arranged at different distances from the nucleus.4.1.1.4 Relative electrical charges of subatomic particles.4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes.4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table.RSC Yusuf Hamied Inspirational Science Programme.Introductory maths for higher education.
The physics of restoration and conservation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
